January 21st, 2020 | by Martyna Mrozek
The UX Design Strategy in the Software Development Process
Table of contents
Why are UX design strategy and human-centered design important in the software development process? Because design helps create products that truly add value and serve people, not computers. Good UX design will simplify tasks and make everyday lives easier. Every founder or CEO, and every UX designer alike, should always think about the impact the design will have on the overall user experience. If the product or service design isn’t easy to use, doesn’t solve problems, and isn’t aligned with natural human habits and market tendencies, it’s destined to fail.
If you want to avoid this scenario, read this article in which we explain the following:
- what the term ‘user experience design means
- what makes user experience design great
- why we need user experience design
- the complete process of designing user experience and examples of useful tools
- why empathy is key in the UX world
We also include some statistics that are helpful in understanding the importance of user experience and good design. Let’s delve straight into the definition of UX design.
MAKE UNFORGETTABLE USER INTERFACE DESIGN WITH US
FILL IN THE FORMWhat is UX design?
User experience (UX) can be understood as a net force of psychology (behavior and mind), sociology (social relationships, social interaction, and culture), and new technologies expression (programming, applications, digital products or services, software, hardware). UX design is focused on the interaction between a user and a product and is oriented at maximizing the ergonomics of this communication. User experience design is the process that encompasses all aspects of the interaction design between the end-users and the company, its services, and its products.
Every user experience design project is based on a deep understanding of users, their needs, values, as well as their abilities and limitations. It is oriented at increasing customer satisfaction by improving the level of design usability and pleasure provided through the interaction between a customer and a product. In the simplest words, UX design is about making the user’s connection to the product the best it can be and creating a user journey through the product or service as easy and productive or fun as possible.
What makes UX design good?
Good user experience is making people feel great. It’s what allows them to simply enjoy using a product or service and keep coming back because:
- it offers great usability, which means that using it is easy, clear, and intuitive
- they find it useful, in that it solves their problems or caters to their needs
- they perceive it as visually attractive and take pleasure in using it
In contrast, the poor user experience will confuse users and cause frustration when they struggle to find features they are looking for or realize that doing what they intended to do is rather difficult or takes a long time. If using a new tool requires research or training before they can navigate it, they will eventually abandon it and opt for a different solution. The market is rich and options continue to multiply, so amid the abundance of choice, users will be looking for solutions that best work for them and allow them to do what they want with ease.
To design great UX, start with user research and study the purpose of the website or application and end with creating the user journey that allows achieving this purpose in the best possible way.
Why do we need UX design?
UX design keeps users happy
The basic reason for any UX design is to increase the quality of the user experience. Great UX design improves the adoption of the product. If the UX design of a website, product or service is successful, business owners will enjoy two important benefits: happy customers and increased sales. To achieve these benefits, we should be oriented at aligning the goals of the user experience with the goals of the business.
For instance, if a user’s experience goal is to perform some sort of action, then the business goal is to facilitate that action – and a UX designer has to make that task as easy and attractive (to give the user some pleasure in contact with the product) as possible. Achieving this user experience goal will bring business profits: a satisfied, well-informed user will return; a frustrated one will not.
People ignore design that ignores people.
Frank Chimero
UX design increases revenue
A solid UX strategy will not only increase your conversion rates and attract new users but can also reduce the number of expenses you’d have to make as a result of poor user experience. Think about the necessary customer support – with an excellent user interface design that is intuitive and easy to use, your customers will simply need less support and you could thus cut business expenditures in that area. Excellent customer experience will also help retain the newly acquired customers and convince them to commit to regular payment plans.
UX design reduces development costs
The undisputed advantage of UX design strategy in the software development process is the reduction of development costs. UX designers help to keep a project within a budget, saves time, and diminishes software development costs. User research, prototyping (in this article we described why low-fidelity prototype matters), and usability testing mean that development time is focused on the functionalities that really matter. This focused approach to interaction design means less risk of feature creep, a good choice of relevant content, and better product design specifications – which are helpful for the front-end development team as well.
UX design guides software developers
Because of UX design, programmers can keep their attention on the functional logic and technical implementation, instead of visualizing the user interface. Good UX design specification documents (detailed documents, which provide information about a product, such as UI design details and technicalities: colors, fonts and measurements, interactions, flows, behaviors, and functionality, etc.) can be used as the base guideline documentation for developers. It can help them in communication and cooperation with each other and to stay focused on their own part of the work, keeping their valuable time safe and helping them to feel more confident at project design. In other words, UX design takes care of the software development team and guides it throughout the project duration.
UX design improves other business metrics
The work invested in creating easy-to-use products which also appeal to users through aesthetic visual design will quickly pay off in a handful of different business metrics. These include user retention, customer loyalty, and productivity. Great design and interface will certainly make users more interested in your product and get them to spread the word about it, eventually increasing your customer pool.
UX statistics you should know
Data really says it all.
If the above points haven’t convinced you yet, take a look at the below sample of statistics to understand why great UX design is crucial for wide product adoption and website traffic:
- first impressions matter: as much as 75% of online users judge a website based on its look and feel
- investing in UX brings substantial ROI: companies that routinely focus on improving their UX and UI designs, observe a $10-$100 return for every dollar invested
- poor UX is a huge discouragement: 88% of online shoppers claim they won’t return to a site after a bad experience and 67% judge a brand negatively based on a poor website experience
- if your website isn’t optimized for mobile, people are 5 times more likely to abandon completing a task on it
In addition to these numbers, it’s worth mentioning that as much as 45% of companies don’t conduct user testing – don’t follow their suit! Statistically, you only need to conduct research on 5 people to learn how to fix your website!
UX design – the process
The UX design is all about ensuring that every aspect of a user’s experience with the product happens with conscious and explicit intent. This means a UX designer has to consider every possible action the user is likely to take and arrive at an understanding of the user’s expectations or desires at every step of the way through that process.
The UX design strategy can be divided into six key phases: understanding, researching, analysis, wireframing, prototyping, and evaluation.
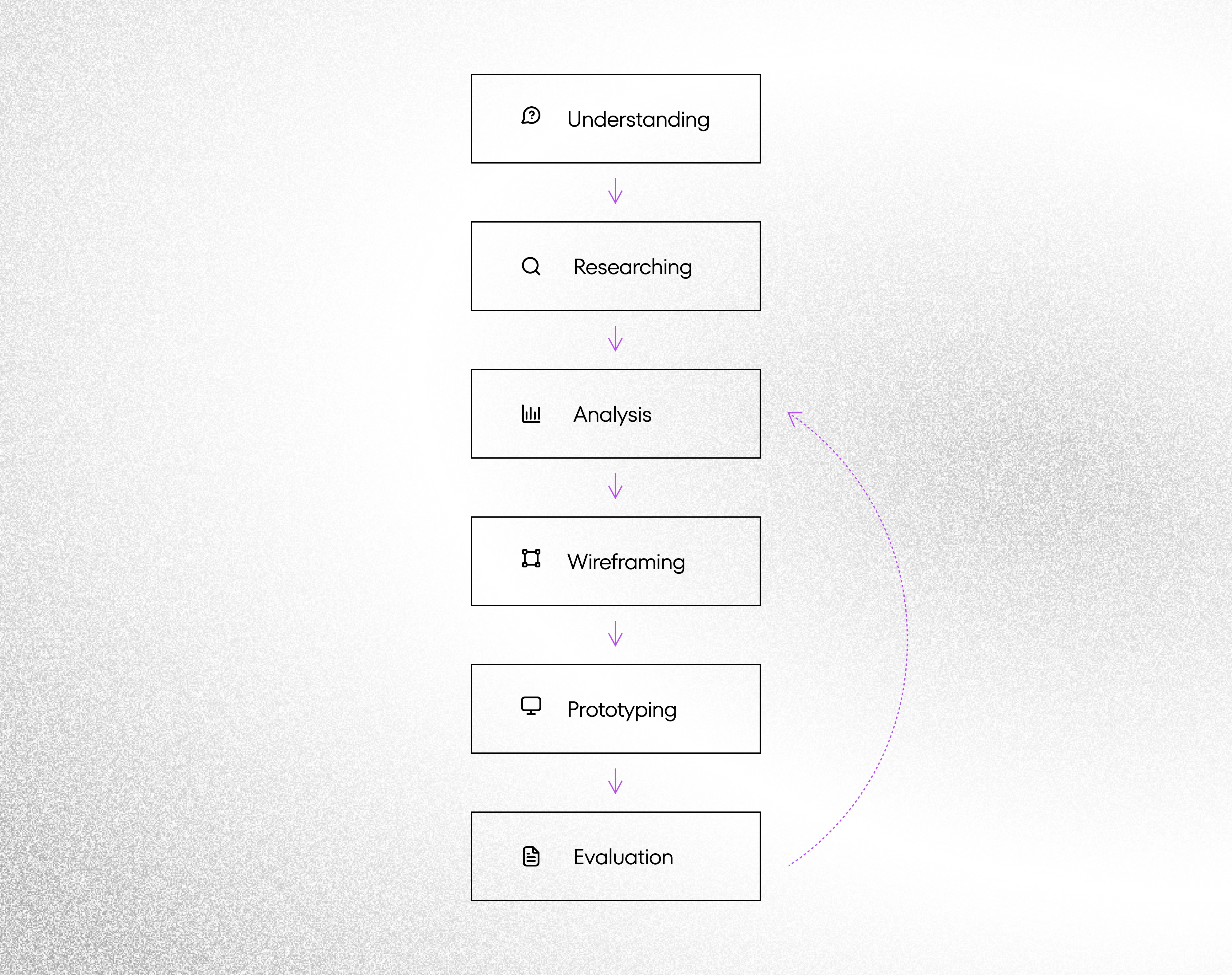
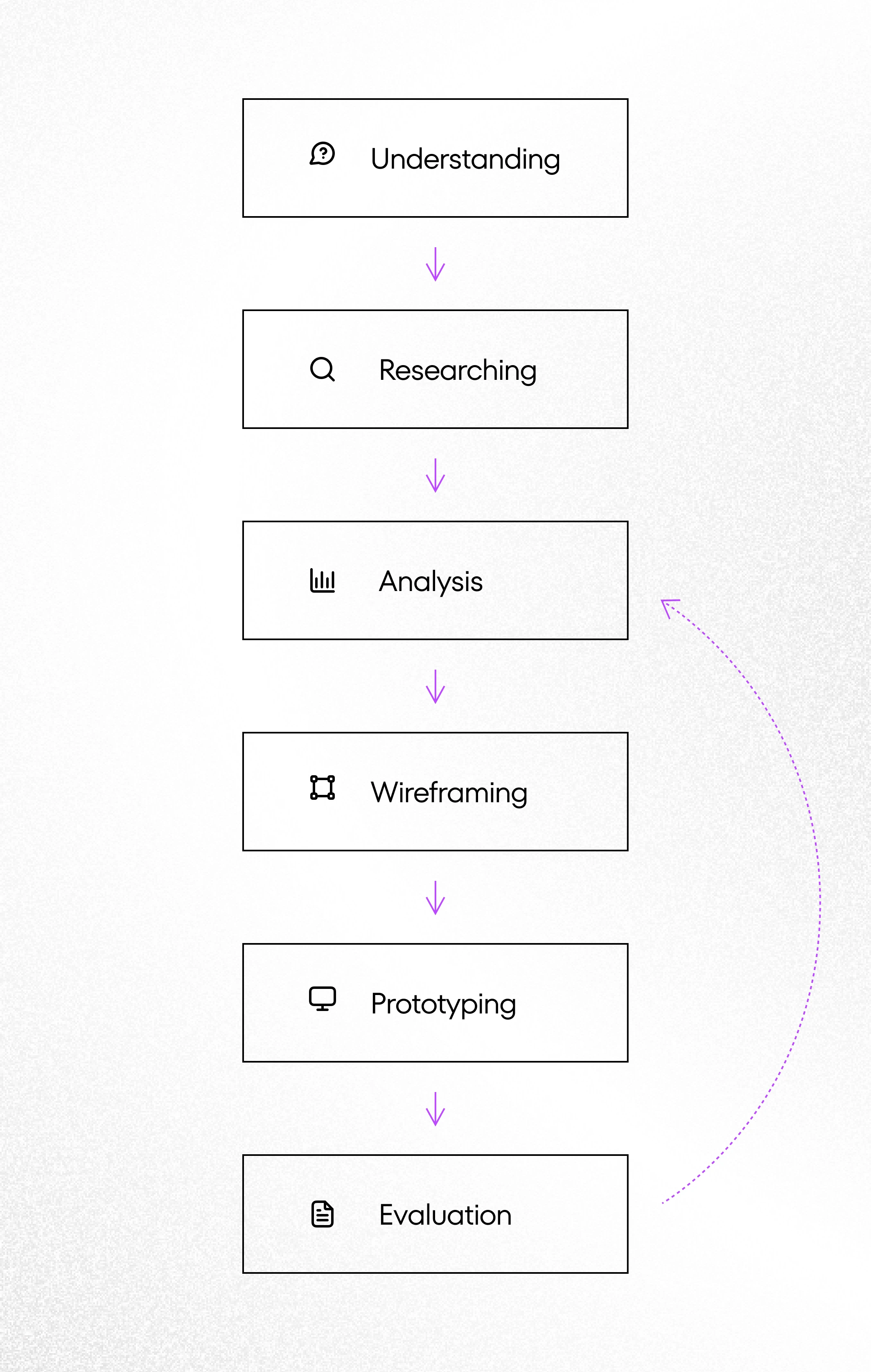
While the design process typically takes place in that order, it’s important to remember that UX design is an iterative process. It is necessary to check the usability level of the designed product after the whole process and make changes if necessary.
Let’s take a closer look at each stage of designing the user experience.
1. Understanding
UX design is about solving problems that users face on a daily basis. When UX designers don’t understand their audience, they fail to see the issues it faces and end up designing products or services for themselves. Good UX design will always focus on people, not the business. However, every brand must also understand why it is the one to solve these specific problems or provide answers.
UX designers need to also study the market in which the new product or service will be used. Every UX designer is required to define real user issues and to apply design skills to solve them. Luckily, the mobile and web market is currently rich, which indicates a high demand for new products and services.
Methodology
What are the problems your potential users are trying to solve? What issues do they face? What do they need help with? What are their likes, wants, and desires? Is there a bigger goal they strive to achieve without realizing it’s possible? Perhaps there are other products that somewhat help them solve their problems? These are just some of the questions UX designers should be asking in order to generate relevant ideas that will ultimately translate into beautiful visual design and excellent user experience. Observation must become a full-time job.
Outcome
This phase should result in defined user experience design goals – the goals that will guide UX designers in creating a strategy for design success.
2. UX research
You cannot build a user-centered design (in this article we answer the question on how understanding the user affects the product design process?) with adequate information architecture without thorough research (both qualitative and quantitative). UX designers should always start with in-depth user research that will help them understand what users try to achieve with a digital product or service and offer adequate solutions. This phase is crucial for contextualizing the overall interaction design.
Methodology
To achieve this goal, UX designers must first study the very core of the problem(s). In this phase, a UX designer carries out contextual and individual interviews, observes users in a real environment, and analyses the competition. Conducting brainstorming workshops with the clients to understand users, their needs, behaviors, motivations, user’s goals, and learn about their perspectives is invaluable in this research phase.
Outcomes
User research shall conclude with visualizations of the requirements of the target group and a definition of the user persona. Designers can create empathy maps, which outline what people said, thought, or felt throughout the study, as well as user journey maps. These will subsequently be analyzed to extract relevant insights for the UX design.
Useful tools
There are plenty of different tools that make visualizing data easy. Tableau is just one of them. Its Public version is available for free and offers a wide range of visualizations. Datawrapper is another tool designers could consider when working directly with clients, or InstantAtlass if you’re looking to create visuals with mapping.
ARE YOU LOOKING FOR PRODUCT DESIGN TEAM?
FILL IN THE FORM3. Analysis
In the UX design analysis stage, the UX designer uses all the information gathered in the previous phase to analyze and find data that will fuel the UX design. This is a moment for gathering insights and generating ideas based on the data collected during research.
Methodology
In this phase, UX designers apply design skills to create a general shape of the product by translating collected data and users’ needs into specific functionalities. Every UX designer must think about the user’s journey through the product, so consulting visualizations such as user journey maps is essential. In this stage empathy and creative thinking are the most important values – they help to drive innovation to our design.
Useful tools
The most popular of all web analytics tools is of course Google Analytics. It’s free and offers a handful of prescriptive and predictive analytics. It is very helpful in understanding user flows and trends, but you may have to watch a tutorial to make the most of what this tool has to offer. If you want to study different segments and funnels on your website to get a better understanding of user journeys, opt for Woopra.
Darshan Somashekar, former VP of Product at Chegg and founder of Spider-Solitaire-Challenge suggests using screen recording tools.
“We use tools like Hotjar which allow us to see user mouse movements and how they interact with our site. You can directly see what’s confusing and address it. Using it, we improved the engagement rate for our spider solitaire and brain training games by 21%.”
Outcomes
As a result of the analyses, a UX designer can create basic UX sitemaps and use cases. They can also produce user journey maps and user stories to study user flow, which will be useful in the subsequent phase.

4. Wireframing
After the UX analysis, it’s time to dress up insights from the previous stages in the low fidelity skeleton of the product – wireframes. UX designers use wireframing to design digital products at a structural level. A wireframe is generally used to layout content and functionality on a graphical user interface (GUI), which considers user needs and user journeys. It happens in an early stage, and it serves to establish the basic information architecture, navigation design, and interface design before adding the visual layer and content.
Methodology
The most important benefit of wireframing is that it provides an early version of the product for you to review with both your internal and external stakeholders. Adjustments can be made easily to the wireframes before moving on to the more complicated process of technical development.
A lot of times people don’t know what they want until you show it to them.
Steve Jobs
Useful tools
There are several useful tools designers can choose from. One of the best options for a smaller budget is Mockplus, but it may not be ideal if you’re looking to create high-fidelity wireframes. NinjaMock is another tool that may be particularly useful for distributed teams that need to collaborate in designing and testing mobile apps and websites. If you’re looking for a free wireframing tool, you can get FluidUI or MockFlow, but bear in mind that they offer limited functionalities.
Outcomes
As a result of this phase, designers will produce UX Sitemaps that demonstrate information architecture, as well as low-fidelity wireframes.
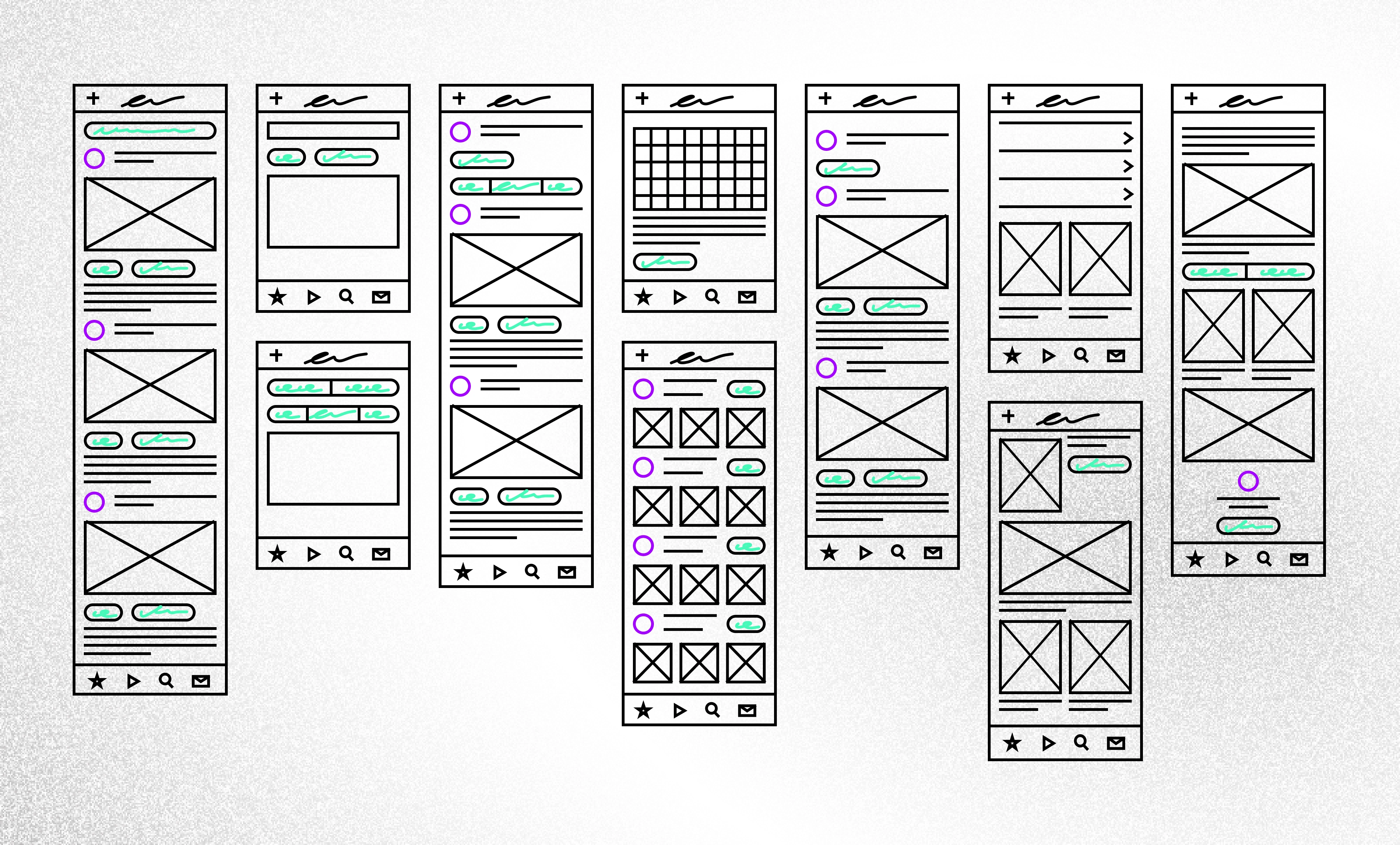
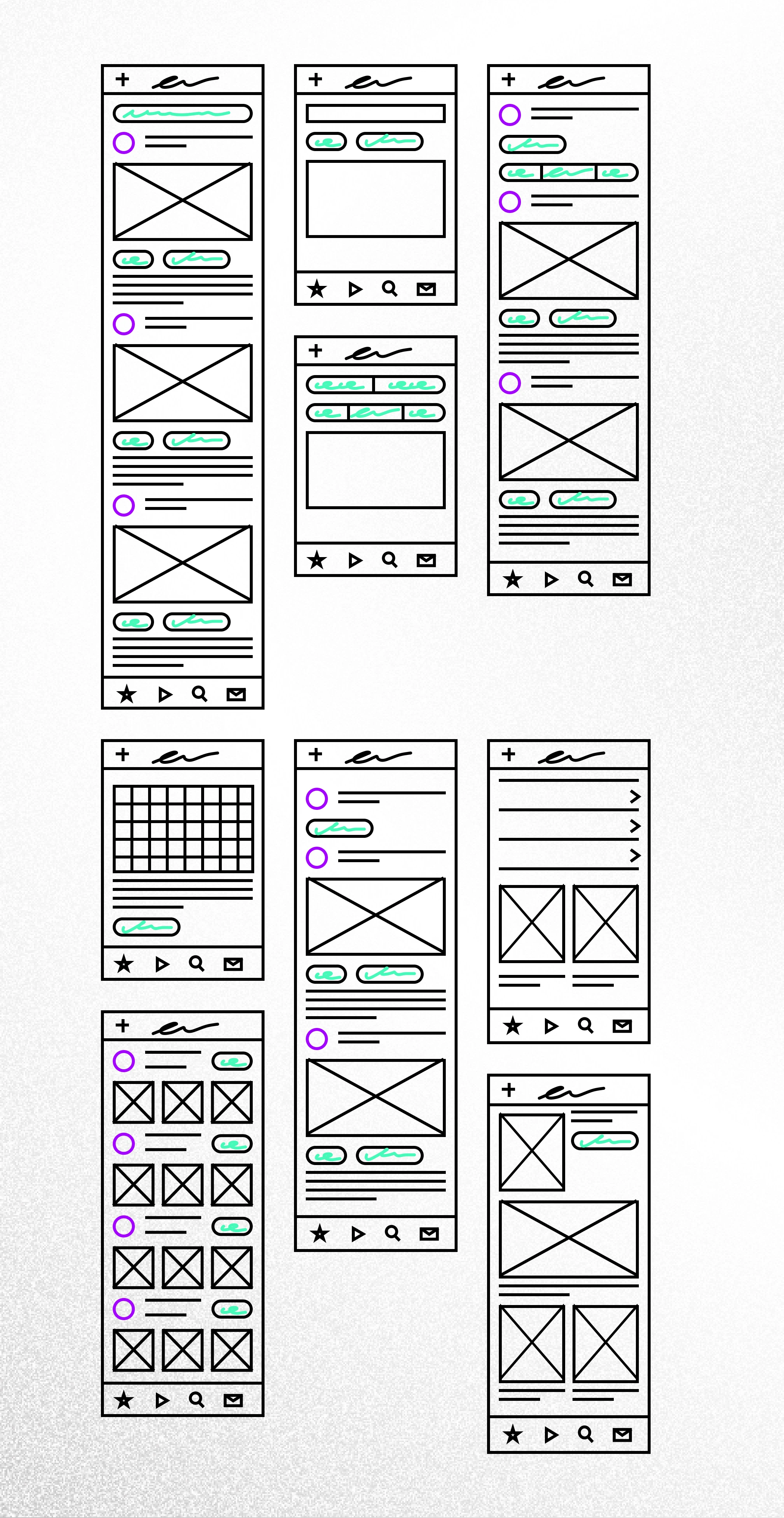
5. UX Prototyping
Essentially, a prototype allows the project stakeholders to see what the final product design will look like early in the project lifecycle; it is a draft version of the product that takes stakeholders as close as possible to a good representation of the final user interface before any coding. The prototype is more detailed than wireframes.
There are many reasons for building prototypes: to test theories and ideas regarding the layout and structure of the product or website, to gain agreement on what is in and out of the scope, to generate support or even investment for the project, to gather user feedback through usability testing, and to help frontend developers in their work. Prototypes help save money and time.
Methodology
Usually, prototypes already are in high visual fidelity — they contain graphic elements of product branding. Sometimes they are clickable and interactive, which allows users to navigate from page to page and use functionalities such as pop-ups or drop-downs.
Useful tools
UX prototyping solutions abound, so every designer will find something that will work for them. The sketch is one of the most popular tools because of its great user experience (no pun intended!). Figma is perfect for collaborative projects, InVision can quickly transform static designs into interactive prototypes, Adobe XD enables easy rescaling and resizing thanks to its vector-based system.
Outcomes
UX designer will produce a high-fidelity prototype, which will demonstrate the features and functionalities of the end product. That prototype will be subsequently evaluated against the business goals.
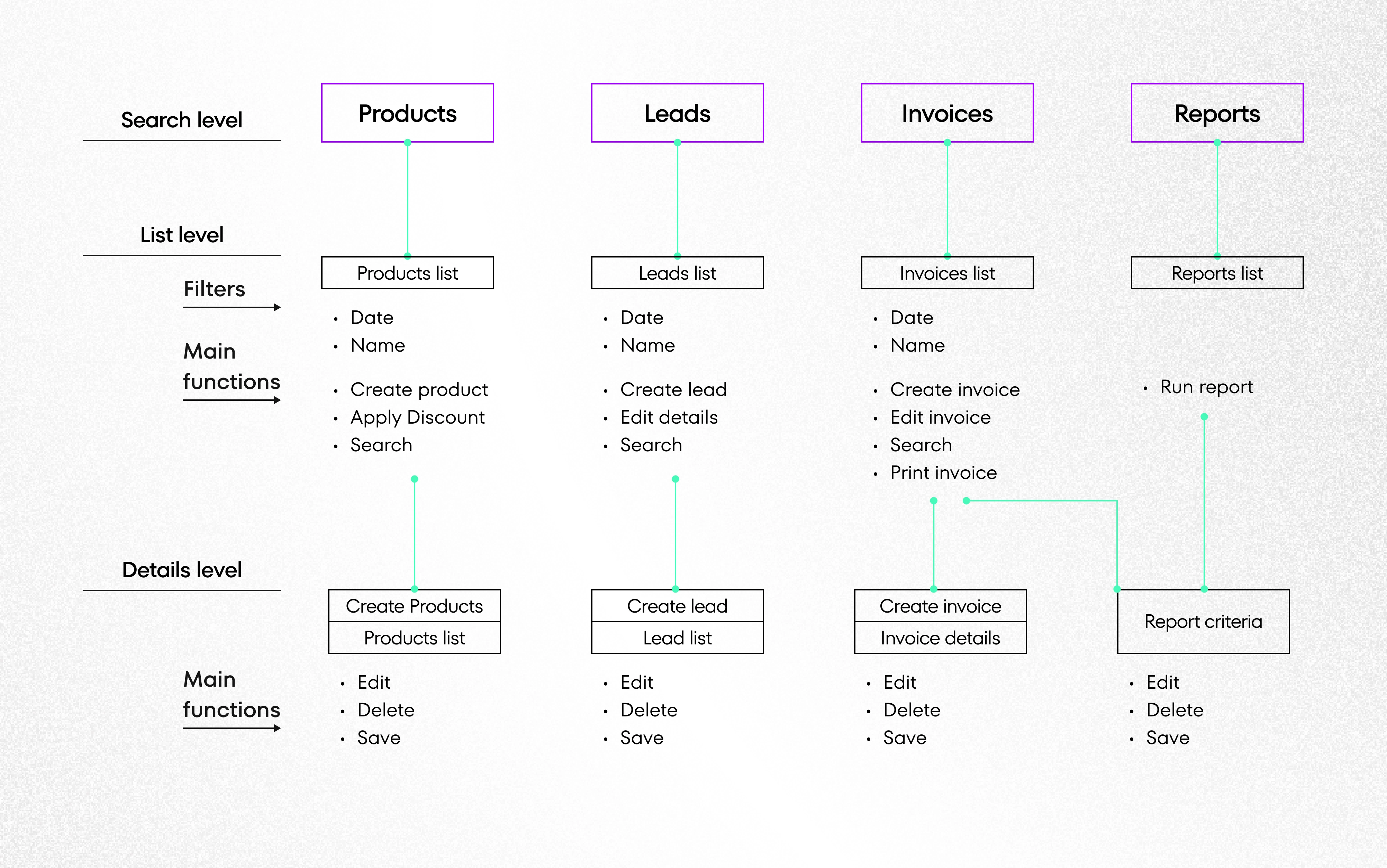
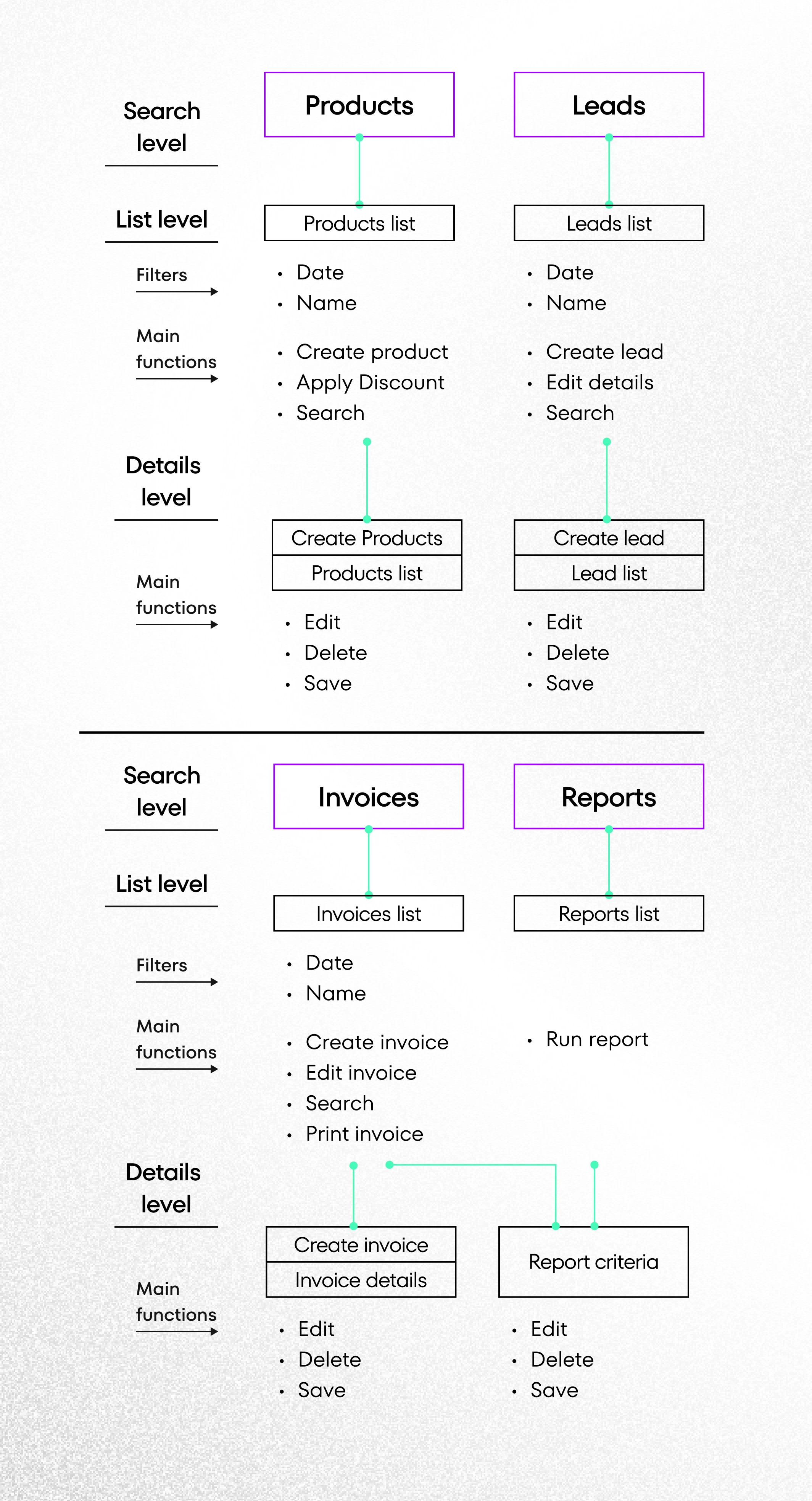
6. UX Evaluation
The evaluation phase in the UX design is all about user testing. It is time to check whether the system requirements defined in the initial phases were addressed in a useful way, so this process is very important for product development.
Methodology
In this phase, a UX designer meets with end-users once again to conduct usability testing workshops with them. The purpose of these workshops is to identify communication problems or issues the user’s experience when they interact with a UI interface and to find out why such problems arise. If you don’t know what elements the UI design should include, read about User Interface Design Fundamentals.
Outcomes
This study should give designers concrete ideas as to what needs to be improved to elevate customer experience and satisfaction.
Empathy is key in the UX design world
The measure of a good UX design is the simplicity of the product’s usability. Even the most complicated ideas can be presented simply enough for everyone to understand, accept, and adopt. If the product or website design you’re working on is complicated due to a subject (financial, economic, medical, law-related issues) or is rooted in an unpopular field, it only means that the UX designer is facing a challenge to present theoretically “uneasy” data in a way that can be easily understood by the end-user.
How to achieve straightforwardness in the design process? The simplest solution is to remember for whom we are designing and to put the end-user at the center of our project. User experience design strategy is a method in which users have a deep impact on a design by being involved as partners of UX designers throughout the whole process of design.
We have to remember that users are people. They have their own expectations from the product or website; they probably want to use the tool to help them solve specific issues or simply do something. Every UX designer must empathize with them, study their needs, likes, limitations, and expectations. The father of the UX design process, Don Norman said:
Design is really an act of communication, which means having a deep understanding of the person with whom the designer is communicating.
Donald A. Norman u0022The Design of Everyday Thingsu0022
Today, we can find many popular methodologies of designing usability, for example, user-centered design / human-centered design, human factor studies, usability engineering. Their common features understand the feelings and potential problems of end-users (which means empathize with them) and similar iterative processes.
UX design – Summary
UX design strategy puts end-users at the very center of the process – it is always focused on having a deep understanding of users, their needs, values, abilities, and limitations.
It is the process of increasing customer satisfaction by improving the level of usability and offering a pleasant interaction between a customer and a product or a website. For these reasons, empathy is one of the most important values in the UX world – it’s what helps to create truly user-centered products or services.
UX design can be categorized as an iterative, multi-stage problem-solving design process that doesn’t involve UX or UI designers only. Analyzing and envisioning the way users are likely to utilize a product, validating their expectations through user testing, and looking at their behavior within user interfaces to identify areas for improvement are also vital parts of the UX creation process that will engage other personnel as well.
UX design strategy is very helpful in software development because it helps to keep a project within budget, save time, and reduce development costs.
UX design makes developers’ lives easier because it helps them communicate and cooperate effectively. It relieves developers from visualizing the UX interface and lets them stay focused on functional implementation.
Read next: The Battle of UX vs. UI Design: Looking Through Product Designer’s Eagle Eyes


